Odds
The odds of an event is simply the probability of the event occurring divided by the probability of the event not occurring.
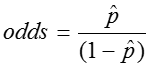
From the above example, in which there were 124 children and 23 of them had colic, we found
![]() , so
, so
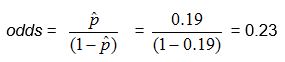
Another way to think about the odds is the ratio of the number in the sample who have the trait or outcome of interest to the number who do not.
Substituting in for p, where x is the number in the sample who have the trait or outcome of interest, and n is the size of the sample,
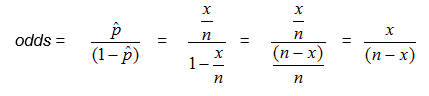
In our example, we can compute the odds directly as the ratio of the number of babies with colic to the number with no colic:
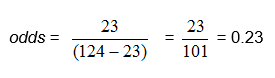
Exercise: Complete the table below and calculate the odds in the table.
|
p |
1-p |
odds |
|---|---|---|
|
0.9 |
||
|
0.5 |
||
|
0.3 |
||
|
0.1 |
Note that if p is small, (1-p) is very close to 1, so the odds, p/(1-p), is a reasonable estimate of p.
