Nurses
Snapshot of Nursing in the US
- Largest healthcare profession at 3 million RNs (4 times the number of physicians)
- Single largest component of hospital staff
- Predominantly a female profession and does not mirror the US population in terms of racial/ethnic diversity
- Lacks standardized education, training and scope of practice
|
Employment Settings of Registered Nurses*
*Percents may not add to 100 due to the effect of rounding. Only RNs who pridived setting information are included in the calculations used for this figure.
|
Nurses and allied health professionals work in a variety of settings including, but not limited to: hospitals, nursing homes, private practices, ambulatory care centers, community, and migrant health centers, emergency medical centers, managed care organizations (MCOs), workplace settings, government and private agencies, clinics, schools and colleges, retirement communities, rehabilitation centers, as private-duty nurses in patients' homes, and as clinical researchers.
Nursing Career Path
The career path for nurses is complicated by the fact that nurses are classified by both education (from a hospital school, college or university) and licensure (by individual states). There is increasing pressure from academic institutions and from accrediting organizations (Magnet) to make the BSN (Bachelor of Science in Nursing) the entry degree.
Source: AARP and RWJF, 2010.
APRN: Advanced Practice Registered Nurse
APRN: Advanced Practice Registered Nurse
SNF: Skilled Nursing Facilities
The lack of clarity on who is a nurse and how to become a nurse created problems in the workplace and in student recruitment efforts.
|
What are APRNs?
Types:
APRNs: Nurse Practitioners (NPs)
|
For this course, when I talk about nurses, I am referring to RNs, unless otherwise specified. When I refer to APRNs, I am grouping together the advanced practice nurses including nurse practitioners, nurse midwives, and nurse anesthetists.
The distinction between registered nurses and APRNs is especially important and this influences scope of practice. You can see above that over time the proportion of nurses with diploma training has decreased, replaced by greater proportions of nurses with associates or bachelors degrees. A Master's degree is now required for all APRNs, and there is talk of the Doctorate (DNP) becoming the entry to practice degree for NPs in the near future.
You may find this Nurse Licensure Map to be a useful summary.
Brought to you by Nursing License Map and Nursing@Georgetown.
Source: http://nursinglicensemap.com/pathways-in-nursing-infographic/
Impact of Nursing
Consider this in terms of quality, cost and access.
Quality: Evidence that care by RNs is associated with patient outcomes
Many recent studies point to the connection between adequate levels of registered nurse staffing and safe patient care.
- Researchers find that nurse staffing levels are associated with fewer deaths, lower rates of infection, and shorter hospital stays.
- Researchers find that insufficient nurse staffing is related to higher patient mortality rates and that when a nurse's workload increases because of high patient turnover, mortality risk also increases.
- Studies confirm that education level and patient outcomes are linked. Efforts to address the nursing shortage must focus on preparing more baccalaureate-prepared nurses in order to ensure access to high-quality, safe patient care.
- The shortage of registered nurses, in combination with an increased workload, poses a potential threat to the quality of care. Increases in registered nurse staffing are associated with reductions in hospital-related mortality and failure to rescue as well as reduced length of stays. In settings with inadequate staffing, patient safety is compromised.
- Most hospital RNs (93 percent) report major problems with having enough time to maintain patient safety, detect complications early, and collaborate with other team members.
- Advocates believe more nurses at the bedside could save thousands of patient lives each year. Studies have shown that every additional patient in an average hospital nurse's workload increased the risk of death in surgical patients by 7 percent. Having too few nurses may actually cost more money given the high costs of replacing burnt-out nurses and caring for patients with poor outcomes.
Cost: Evidence that care by RNs and APRNs is cost savings
- Use of RNs and NPs in transitional care and chronic illness management programs reduces utilization of more expensive services.
- Nurse midwifes tend to use fewer resources for prenatal care and labor
- The PCP shortage is pushing patients into emergency departments NPs are licensed to diagnose and treat acute and chronic illness in a less resource-intensive setting (outpatient practices, urgent care, even the Minute Clinics that are cropping up).
- Improved quality of care by RNs as discussed above decreases treatment costs to hospitals, payers and individuals by preventing complications.
Access: Evidence that increased use of RNs and NPs increases access to care
- APRNs can provide acute and chronic care in areas with physician shortages.
- Nurse midwives may do the same where there is insufficient OB coverage.
- In ambulatory settings RNs can see patients for disease education visits and immunizations.
The Nursing Shortage
The nursing shortage can be examined from four different perspectives:
- increasing demand for nursing
- decreasing supply of nurses
- challenges to solving the problem
- possible solutions.
Increasing Demand
- Creation of new jobs and expanding roles
- Primary care MD shortage
- The aging US population will need more healthcare
Decreasing Supply
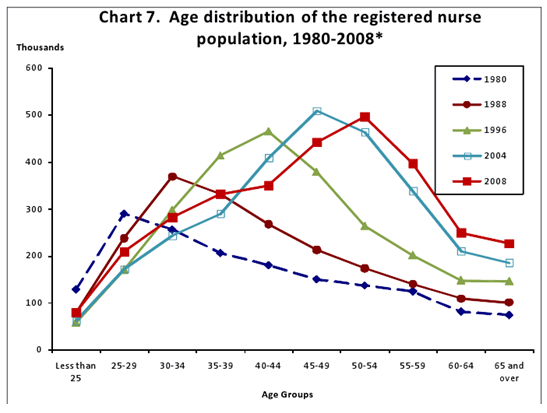
- As the population ages so does the nursing workforce. See the chart below. It is estimated that about half the nursing workforce would like to retire in the next 10 years.
- When the economy improves it is thought that nurses of all ages will leave the workforce or cut their hours if other family members are able to bring in more financial support.
|
US DHHS 2010 from National Sample of RNs
Source: bhpr.hrsa.gov/healthworkforce/.../rnsurveyinitial2008.pdf |
Challenges
- Recruitment
- Women have more education and career options
- Confusion surrounding types of nursing and roles
- Public opinion of nursing
- Not attracting men or minority candidates
- Education
- Educational Institutions
- Pays more to be a nurse than to teach nursing
- 67,000 qualified applicants were not able to enroll in baccalaureate and graduate level nursing programs due to program constraints, mainly related to faculty shortages (2010 survey. American Association of Colleges of Nursing).
- Retention
- RNs may have common license, but certain patient care areas require specific skills. Replacement is not always easy and can be expensive
- 18% of new RNs left their 1st job within 13 months.
- It is expensive to orient new staff RNs
- Why do nurses leave their jobs or leave nursing altogether? Dissatisfaction.
- Unhappy with the hours
- Stress or burnout from physical and emotional workload
- Climate of patient care unit
- Workplace safety
- Staffing and associated safety concerns
Solutions
- Recruitment and education
- If BSN will be the standard then make it financially feasible
- Facilitate graduate education
- Financial incentives to produce more faculty
- Outreach to underrepresented groups
- Enable existing hospital employees to pursue nursing education
- Programs for nurses to reenter the workforce
- Retention through improved work environment
- Consider cost, quality, and nurse satisfaction
- Legislate minimum staffing ratios and prohibit mandatory overtime
- Design of jobs and worksites
- Career ladders
- Improve workplace safety
- Collaborative work environment
The figure below shows a health policy solution. Individual states have begun to propose legislation for staffing standards for inpatient care.
|
President Obama Addresses the Nursing Shortage Source: http://youtu.be/N2R6vRn0p9I |
Federal Legislative Solutions
Nurse Reinvestment Act of 2002
- Funds to educate nurses, load repayment for faculty, geriatric training grants
- Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009
- Funded nursing education and retention programs
- Patient Affordable Care Act of 2010 (in this class we refer to PACCA as the ACA)
- Loan repayment programs (60% for 2 years worked in underserved area)
- Expand funding for APRNs
Conclusion for Nursing
- The demand for nursing will continue to grow.
- Need to come up with solutions to increase the supply.
- Reducing waste will maximize resource use and hopefully improve the work experience.