Overview of Project Management
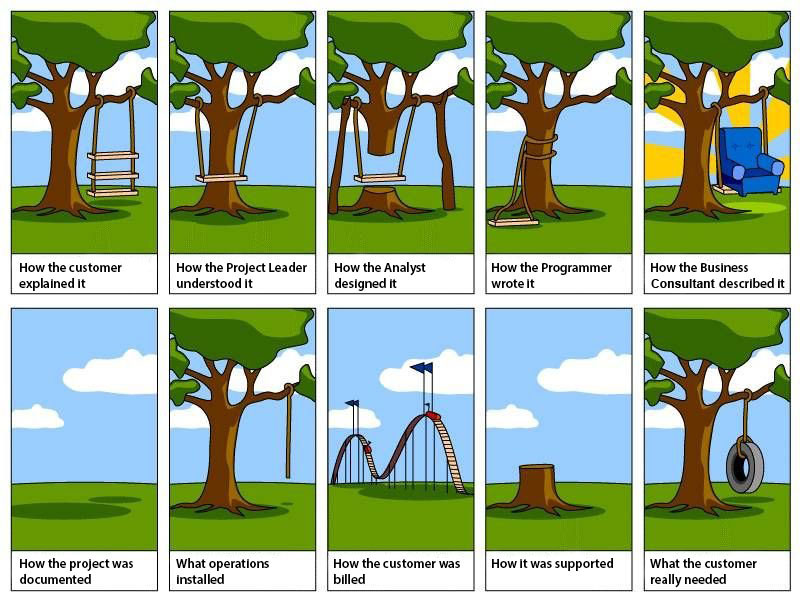
This illustration below describes one of the most common and well-understood pitfalls in project development, namely the different perspectives that the various roles in project development bring to the task at hand. The goal of project management (and of this module) is to limit this problem by bringing together a collection of tools and processes to get all stakeholders on the same page.
Steps in Project Management
An overview of the steps in project management is provided below. While this module is concerned principally with the first three steps (identification, formulation, and planning), it is important to keep all the steps in mind. Note that not all steps are applicable to every project, and that each step may be modified to fill the needs of a particular project.
Select each section below to learn more about the steps in project management.
Project management is a basket of many tools. For the purpose of this module, we will address two of those tools: the project charter and gantt chart respectively. Continue to the next page to learn how to develop a project charter.