
Technology and Drugs
|
|
This module focuses on technology and the FDA. Medical technology might be broadly defined as any scientific discovery that finds its application in delivering health care. In essence, it results from the application of scientific knowledge produced by biomedical research and adapts certain developments from other scientific fields, such as chemistry, physics, engineering, etc. This broad definition, then, embraces drugs, equipment, devices, information systems, and surgical procedures.
It was not very long ago that families had nothing more than thermometers and heating pads as their diagnostic and treatment tools at home. Now they have sophisticated, yet portable, equipment, devices, radiofrequency technology, and computer systems to monitor their heart and lungs, test their blood sugar levels, administer medications, and improve their levels of independent functioning within their own environments.
Although we are seeing increasingly sophisticated medical technology in the US and other developed countries, further advances are constantly being made. As a result of the addition of medical nanotechnology to existing knowledge of molecular and cellular biology, it is likely that new, more personalized, more accurate, and more rapid diagnostic techniques will be devised in the future.

Technology diffusion can be defined as the process by which innovations are adopted by a population. Whether diffusion occurs and the rate at which it occurs is dependent on several factors including the nature and quality of the innovation, how information about the innovation is communicated, and the characteristics of the population into which it is introduced. Americans have come to demand state-of-the-art medical technology, despite its astronomical costs, and we place a huge emphasis on medical specialization. As we have seen, the coverage of health services by insurance companies actually creates a moral hazard to use high-cost services. And keep in mind "supply-side" competition—which can result in duplication of services and equipment.
The mission of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) is to promote policies that will improve the economic and social well-being of people around the world. The OECD provides a forum in which governments can work together to share experiences and seek solutions to common problems.
|
|
You may want to browse the OECD site to see how other member and partner countries compare.
The term Information Technology (IT) refers to an entire industry that uses computers and software to manage information. In some companies, this is referred to as Management Information Services (MIS) or Information Services (IS). The information technology department of a large company would be responsible for storing information, protecting information, processing the information, transmitting the information as necessary, and later retrieving information as necessary.
Applications of Information Techology
A brief definition of "informatics" is "information, communication of knowledge, transmission of knowledge, dissemination, diffusion." Health informatics is a rapidly emerging discipline within the health care system, and goes far beyond computer management of data. A slightly broader definition is "the knowledge, skills and tools which enable information to be collected, managed, used and shared to support the delivery of health care and to promote health."
Source: NHS Careers

Our world has been radically transformed by digital technology – smart phones, tablets, and web-enabled devices have transformed our daily lives and the way we communicate. Medicine is an information-rich enterprise. A greater and more seamless flow of information within a digital health care infrastructure, created by electronic health records (EHRs), encompasses and leverages digital progress and can transform the way care is delivered and compensated. With EHRs, information is available whenever and wherever it is needed.
http://www.cms.gov/Regulations-and-Guidance/Legislation/EHRIncentivePrograms/index.html?redirect=/ehrincentiveprograms/
When fully functional and exchangeable, the benefits of EHRs offer far more than a paper record can. The Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act, a component of the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009, represents the Nation's first substantial commitment of Federal resources to support the widespread adoption of EHRs.
Eligible Professionals Participating in the Medicare EHR Incentive Program
Basic Information
Medicaid also has a program that will not be described here, as specific provisions vary by state.
Change can be difficult. Not everyone is finding the intended outcomes or benefits that were expected. Is this a learning curve or is it indicative of a bigger problem?
Some Excellent Resources
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) was enacted in 1996 to address confidentiality of patient information and to confer certain patient rights with regard to information contained in their medical records.
Watch the following videos:
|
Privacy Rights in Your Health Information Privacy and Protection |
The Internet has made patients more active participants in their own health care. e-Health includes all forms of electronic health care delivered over the Internet (information, education, products, services, etc.)
Other applications include:
The Internet and E-health have seen increased use by patients and physicians. Certain applications can make physicians more productive. For certain health conditions, virtual visits are appropriate for monitoring and follow up. But telemedicine has faced several barriers as well, such as problems with licensure of physicians and other providers across state lines, concerns about legal liability, lack of reimbursement, and questionable cost-effectiveness. But, many remote in-home patient monitoring programs are proving to be cost-effective. So, time will tell, and more research and evaluation will be needed.
Read E-Health Opportunities for Seniors
Connecting more older Americans to the Internet is expected to improve opportunities to protect their well-being and reduce national costs for care.
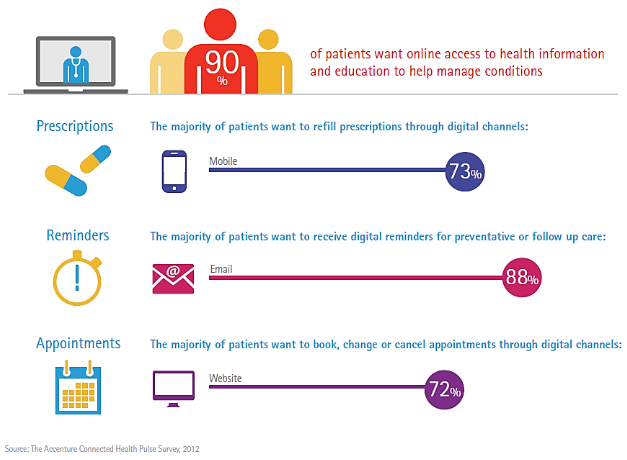
Infographic: Most Patients Want to Self-Manage Healthcare Online
See the following articles on the use of the iPad in the workplace, including health care, as well as the war between iPad, Android, Blackberry, HP, and other medical tablets. Physicians may be ready to use them, but are hospitals and clinical environments ready to accommodate their needs?
Read the following article from the Science secion of the New York Times: Redefining Medicine with Apps and iPads
Keeping in mind the various aspects of medical and information technology, as well as EHR, HIPAA, and privacy issues, let's now expand our discussion to include more real concerns about patient safety, medical errors, and health communication. The use of apps for self-monitoring is becoming more of a controversy on several fronts. One concern is privacy and how much of what an individual enters into an app is shared for commercial interests. Consumers have no HIPAA protection here and there is big money in data mining for industry. How many of us read and think about each word when we agree to a 'terms of use' screen? Another concern is with the quality of the information in the applications. As more consumers use apps in managing health and illness the stakes get higher. Providers use these as well in clinical decision making. On the other hand the ability for an individual to track and compare health behaviors (exercise, sleep, water intake, food diary) is powerful and may contribute to improved health habits. I am personally very motivated (maybe over motivated some days) by my Fitbit. I set goals and complete against myself. I am also a fan of GPS mapping my bike trips and get excited when I see I am getting faster, going further, or that I conquered higher elevation. Other people prefer to share and complete with others on Facebook and other online communities. Currently the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) does not regulate these apps. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) also has a stake, since part of their mission is to protect consumers against false claims to and misleading advertising.
What about use of social media by the health care workforce? Where should lines be drawn? This will continue to be a high growth area and an opportunity for health communicators. Listen to the two brief NPR pieces below.
|
http://www.npr.org/player/v2/mediaPlayer.html?action=1&t=1&islist=false&id=155977692&m=156577709
http://www.npr.org/player/v2/mediaPlayer.html?action=1&t=1&islist=false&id=166240156&m=166381967
|
Telemedicine is a rapidly developing application of clinical medicine where medical information is transferred through interactive audiovisual media for the purpose of consulting, videoconferencing, remote medical procedures, or examinations. Telemedicine generally refers to the use of communications and information technologies for the delivery of clinical care.
Telemedicine has several forms
Telemedicine is seen as a way to increases access to care, especially in rural areas and for the homebound. Challenges in telemedicine include security of information transmission, lack of standards for reimbursement, scope of practice issues if the patient and provider are in different states, and liability.
Telemedicine can extend access to individuals in remote areas or to those patients confined to home. For this week you were asked to read an example from rural areas of South Dakota. Imagine someone you care about needing emergency care and needing to travel 200 miles to be seen by a physician with the necessary training and expertise.
A particularly vulnerable population is veterans receiving care at the Veteran's Health Administration. Remember that VA coverage is generally coverage at VA locations. It is not the same as having an insurance care to use in other locations. Veterans live across the country, including rural areas. VHA facilities are across the nation, certainly not accessible to all.
|
Source: NPR.org
|
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a large role in technology diffusion in the medical field, by:
Watch the interview below with John Jenkins, Director of the Office of New Drugs at the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. Pay particular attention to his comments on quality and safety of approved drugs, including post-approval surveillance.
|
|
What the FDA Does
The United States is the global leader in medical device innovation and the Food and Drug Administration's (FDA) Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) is committed to assuring that American patients have timely access to important new technologies and next-generation products without compromising their safety. Each year, millions of American patients benefit from innovative medical devices that reduce suffering, treat previously untreatable conditions, extend lives, and improve public health. CDRH is responsible for advancing public health and facilitating innovation to help bring novel technologies to market and make the medical devices that are already on the market safer and more effective.
What the FDA does NOT do:
For more information visit the U.S. Food and Drug Administration website.
You can also explore the FDA Drug Approval Process Infographic provided as a Drug Approval Process (PDF). Alternatively, you can view it online.